In the world of finance, understanding how to balance risk and return is crucial for any investor. One of the most powerful tools in this endeavor is the Capital Market Line (CML). The CML is a graphical representation that helps investors optimize their portfolios by combining risk-free assets with risky ones. In this article, we will delve into what the CML is, its components, how it is calculated, and its role in portfolio optimization. By the end of this guide, you will be well-equipped to use the CML to make informed investment decisions.
- How to Profit with a Bear Call Spread: A Comprehensive Guide to This Bearish Options Strategy
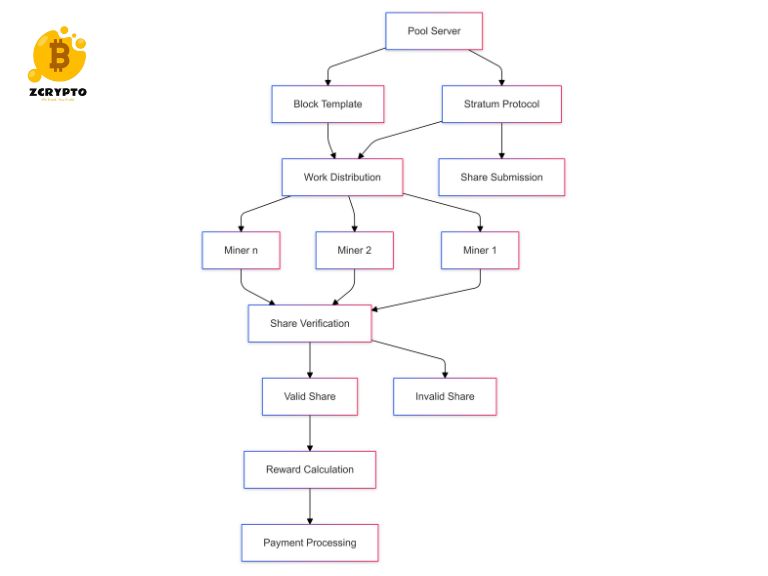
- What is Mining Pool? A Technical Analysis of Collaborative Cryptocurrency Mining
- Understanding Actuarial Gains and Losses: Impact on Pension Plans and Financial Statements
- Databricks nears 9.5 billion mega-investment
- Understanding the Board of Governors: Roles, Responsibilities, and Impact on Finance and Economy
What is the Capital Market Line (CML)?
The Capital Market Line (CML) is a fundamental concept in modern portfolio theory. It represents a set of portfolios that optimally combine the risk-free rate of return and the market portfolio of risky assets. The CML is derived from the efficient frontier, which plots all possible combinations of risky assets based on their expected returns and standard deviations. By drawing a tangent line from the risk-free rate to the efficient frontier, we obtain the CML.
Bạn đang xem: Mastering the Capital Market Line (CML): A Guide to Optimal Risk and Return in Investment Portfolios
The slope of the CML is known as the Sharpe ratio of the market portfolio, which measures excess return per unit of risk. This slope indicates how much additional return an investor can expect for taking on an extra unit of risk. Understanding this relationship is key to making smart investment choices.
Components of the Capital Market Line
Risk-Free Asset
The risk-free asset, typically represented by government bonds or treasury bills, plays a critical role in the CML. These assets offer a return with zero risk, providing a baseline against which other investments can be measured. Including risk-free assets in a portfolio allows investors to reduce overall risk while still earning some return.
Market Portfolio
The market portfolio consists of a diversified set of risky assets such as stocks and bonds. This portfolio represents the entire market and serves as a benchmark for evaluating individual investments. The market portfolio is crucial because it provides a broad exposure to various asset classes, helping to spread risk.
Combination of Risky and Risk-Free Assets
The CML integrates both risky and risk-free assets to provide a comprehensive view of investment options. By combining these two types of assets, investors can create portfolios that align with their risk tolerance and return expectations. This combination allows for flexibility in portfolio construction, enabling investors to adjust their exposure to risk and potential returns.
Formula and Calculation of the CML
To calculate the CML, you use the following formula:
Xem thêm : What is ODL (On-Demand Liquidity)?
[Rp = rf + \frac{RT – rf}{\sigmaT} \sigmap]
Here:
-
(Rp) is the portfolio return.
-
(rf) is the risk-free rate.
-
(RT) is the market return.
-
(\sigma_T) is the standard deviation of market returns.
-
(\sigma_p) is the standard deviation of portfolio returns.
Xem thêm : Unlocking Stock Performance: The Ultimate Guide to 52-Week High/Low
The step-by-step process involves determining the risk-free rate, selecting risky assets, calculating expected returns and standard deviations for these assets, and plotting the efficient frontier. Once you have this data, you can draw the tangent line from the risk-free rate to find your optimal portfolio on the CML.
Role of the CML in Portfolio Optimization
Determining Optimal Portfolios
The CML helps investors determine the optimal mix of risk-free and risky assets to achieve the best risk-return profile. By analyzing where their current portfolio lies in relation to the CML, investors can identify whether they are taking on too much or too little risk relative to their expected returns.
Risk Tolerance
Investors can adjust their portfolios based on their risk tolerance by moving along the CML. If an investor is more risk-averse, they might choose a point closer to the risk-free rate; if they are more aggressive, they might opt for a point further along the line towards higher returns but also higher risks.
Tangency Portfolio
The tangency portfolio is the point where the CML intersects with the efficient frontier. This represents the most efficient portfolio because it offers the highest expected return for a given level of risk. Identifying this point helps investors maximize their returns while minimizing unnecessary risks.
Comparative Analysis: CML vs. CAL vs. SML
Capital Allocation Line (CAL)
The Capital Allocation Line (CAL) represents the risk and return trade-off for any risky portfolio combined with a risk-free asset but does not necessarily involve an optimal combination like the CML does. While both lines help in visualizing portfolio performance, only one—the CML—ensures that you are getting the best possible return for your level of risk.
Security Market Line (SML)
The Security Market Line (SML) focuses on individual securities rather than portfolios. It plots expected returns against beta (a measure of volatility relative to market volatility) for individual stocks or bonds. Unlike the CML, which deals with overall portfolio construction, SML is used more for evaluating specific investment opportunities within those portfolios.
Applications and Utility of the CML
Investment Decisions
The CML guides investment decisions by providing a clear representation of trade-offs between risk and return. By understanding where different portfolios lie on this line, investors can make informed choices about how much risk they are willing to take on in pursuit of higher returns.
Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM)
Within the framework of Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM), which evaluates investment opportunities based on their expected returns relative to their risks, the CML plays a pivotal role. It helps determine whether an investment is fairly priced or if it offers an attractive risk-return profile compared to other available options.
Nguồn: https://horizontalline.icu
Danh mục: Blog